Managed Service Providers (MSPs) face significant threats, particularly to their Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) applications.
Using data from the recent Acronis Cyberthreats Report, this article summaraizes these threats to RMM applications and outlines a concise strategy for MSPs to protect their systems.
Understanding the Threats
Threats to RMM applications include:
- Vulnerability Exploits — Cybercriminals actively seek out and exploit known vulnerabilities in RMM applications to gain access to client systems
- Leaked Credentials — Attackers obtain login information through data breaches or phishing attacks on other systems and use this information to access RMM applications
- Brute Force Attacks — These attacks involve systematically trying different credentials until the correct one is found. Weak or default passwords are particularly vulnerable
- Deployment of Additional RMM Software — Attackers may deploy their own RMM software to achieve persistence and maintain control over compromised systems, which can be challenging to detect if multiple RMM solutions are already in use
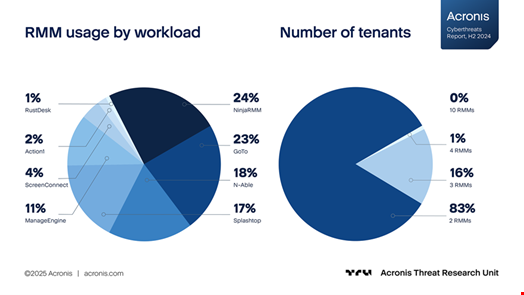
The report also notes that the presence of multiple RMM solutions within an MSP makes it easier for attackers to deploy their own tools without being detected.
The Impact of AI on RMM Security
AI is being leveraged to create more sophisticated and automated attacks, such as:
- Malicious Scripts — AI can generate complex scripts that automate the exploitation of vulnerabilities
- Spear-Phishing Emails — AI-driven tools can craft highly convincing phishing emails, increasing the likelihood of successful attacks
- Ransomware — The report cites an example of a youthful attacker who used ChatGPT to write ransomware in just six hours, demonstrating that low-skilled cybercriminals can now carry out complex operations
These AI-driven threats underscore the need for MSPs to adopt advanced, multilayered defense strategies.
Key Recommendations for Protecting RMM Applications
To safeguard RMM applications from cyberattacks, MSPs should implement the following key recommendations:
- Security Awareness Training — Training, awareness, and vigilence are the first line of defense
- Force Multifactor Authentication (MFA) — MFA is very effecgtive and should be required on all privileged accounts and critical systems
- Employ Network Segmentation — This ensures that even if one part of the network is compromised, the damage can be contained
- Establish Robust Patch Management — Regularly check for and install security updates from vendors like Microsoft, Adobe, and Google to protect against known vulnerabilities
- Implement Data Encryption and Loss Prevention — Force encytption and data loss prevention (DLP) tools monitor and control data access and transfer
- Continuous Monitoring — Continuously monitor RMM applications and the overall network for suspicious activities
- Deploy Advanced Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) — EDR solutions with AI and behavioral analytics detect and respond to advanced threats in real-time.
- Develop and Update Incident Response Planning — Ensure swift detection, containment, and recovery in the event of a breach. Conduct regular drills to test the effectiveness of the plan
- Imlement Automated Remediation — Automation can significantly reduce the time it takes to respond to and mitigate security incidents
- Conduct Post-Incident Analysis — Identify the root causes of security breaches and update defenses accordingly
Implementing Robust Password Management and Regular Patching
MSPs should focus on robust password management and regular patching:
- Enforce Strong Password Policies — Require the use of long, unique passwords and consider implementing password complexity requirements. A password manager can help employees remember and manage these passwords
- Enable Multifactor Authentication (MFA) — MFA should be mandatory for all privileged accounts and critical systems
- Establish a Robust Patch Management Program — Develop a systematic and automated approach to applying updates and security patches
- Monitor Security Bulletins — Stay informed about new vulnerabilities and patches by monitoring security bulletins from vendors like Microsoft, Adobe, and Google
- Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing — Regularly audit RMM application security and conduct penetration testing across the overall network to identify and address any weaknesses
Conclusion
RMM applications are a critical component of an MSP's toolkit, but they also present significant security risks. By understanding the specific threats and implementing the recommended security measures, MSPs can significantly enhance RMM security and protect their clients' systems from cyberattacks. The Acronis Cyberthreats Report H2 2024 provides valuable insights and actionable recommendations that can help MSPs stay ahead of the evolving threat landscape.
For a deeper dive into the most recent data and to learn more about global cyberthreats, readers can download the Acronis Cyberthreats Report H2 2024.
