Three years after its discovery, the Log4J vulnerability (CVE-2021-44228) exploit remains one of the most attempted exploits observed by cloud security provider Cato Networks.
Cato Cyber Threat Research Labs (CTRL) published its inaugural SASE Threat Report for Q1 2024 on May 6 during the RSA Conference 2024.
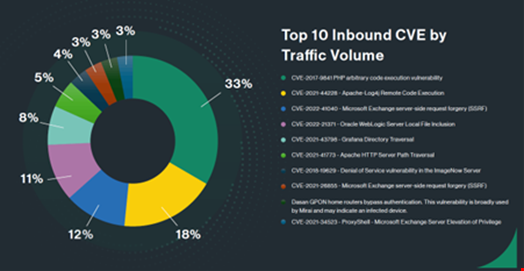
In the report, the firm observed that the Log4J exploit represented 30% of the outbound vulnerability exploitations and 18% of the inbound vulnerability exploitations detected in the first quarter of 2024.
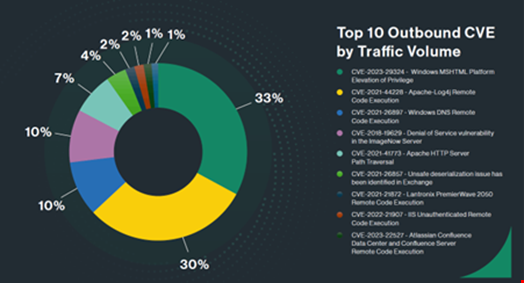
Another old vulnerability exploit, CVE-2017-9841, which targets the PHPUnit testing framework, is the most common vulnerability found to be exploited. According to Cato’s stats, it comprised 33% of all vulnerability exploitations during the reported period.
“While zero-day threats earn much attention in the industry, threat actors often eschew the use of the latest vulnerabilities and instead exploit unpatched systems,” the report states.
Speaking to Infosecurity, Etay Maor, chief security strategist at Cato Networks and a founding member of Cato CTRL, commented: "I'm a cyber nerd, and if you get me started talking about zero-days, I could go on for hours. But in real life, some threat actors don't even need a zero-day exploit. Patching is hard. Yesterday I went on Shodan to search for a particular 2019 vulnerability. I found 2.2m devices exposed on the internet and vulnerable to it."
Insecure Protocols Remain Widespread
Once threat actors penetrate a network, they can often easily move laterally, as most organizations still run insecure protocols within their wide area networks (WAN).
Cato found that 62% of all web applications run on HTTP, a non-encrypted web protocol.
Additionally, 54% of all WAN traffic runs on Telnet. This client/server application protocol provides access to virtual terminals of remote systems on local area networks or the internet. It is known for being vulnerable to network-based cyber-attacks.
Finally, Cato observed that 46% of observed WAN traffic uses version 1 of server message block (SMB), a communication protocol used to share files, printers, serial ports and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network, instead of its more secure versions 2 and 3.
Lateral movement was identified most frequently in the agriculture, real estate, and travel and tourism industries.
Industry-Specific Tactical Trends
Cato also found that threat actors tend to have preferred techniques, tactics, and procedures (TTPs) depending on which industry they primarily target.
For instance, the ‘Endpoint Denial of Service’ technique (tracked as T1499 by non-profit MITRE) is particularly prominent in cyber-attacks targeting victims in the entertainment, telecommunication and mining & metals sectors.
In the services and hospitality sectors, however, threat actors tend to utilize the ‘Exploitation for Credential Access’ technique (T1212), as Cato observed this TTP used three times or more often in cyber-attacks targeting this industry than in others.
Cato CTRL analyzed 1.26tn network flows in the systems of Cato Networks' 2200 customers for this report.
"We are going to publish a similar report every quarter now and we will also publish breakdowns. Our customers can see the threats relevant to them specifically, but now we want to show them what's happening in their industry and in their countries. It's important to prepare for those threats, because they can inform our defenses. A threat actor attacking a car manufacturer in Japan today could target a car manufacturer in Germany tomorrow," Maor concluded.
