Just 3% of organizations are resilient against modern cybersecurity threats, according to Cisco’s 2024 Cybersecurity Readiness Index.
This represented a significant decline in the proportion of global organizations that had a ‘mature’ level of readiness compared to last year, when 15% were ranked mature.
Nearly three-quarters (71%) of organizations fell into the bottom two categories – ‘formative’ (60%) and ‘beginner’ (11%). The other 26% were ranked as ‘progressive.’
The report surveyed 8136 private sector business leaders who have cybersecurity responsibilities in their organizations, analyzing their security posture across five pillars:
- Identity intelligence
- Machine trustworthiness
- Network resilience
- Cloud reinforcement
- AI fortification
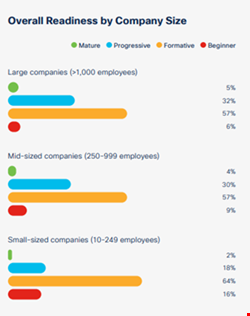
The size of the organization correlated with cybersecurity readiness, with bigger companies exhibiting a higher rate of maturity.
For example, larger businesses (over 1000 employees) scored highest in the top two categories – mature and progressive.
Conversely, small companies (10-249 employees) were significantly less ready, with the highest proportion falling into the formative and beginner categories.
The industries that had the highest proportion of organizations ranked as mature were travel services (4%), business services (4%) and manufacturing (4%). The researchers said this reflects the need to protect the large volume of valuable and confidential information these companies hold for their clients.
The sectors which had the most organizations in the beginner category were personal care and services (18%), education (17%) and wholesaling (15%).
Encouragingly, 91% of respondents said their organization has increased its cybersecurity budget over the past one to two years, with the majority expecting their budget to rise further in the next one to two years.
Majority of Organizations Hit by a Cyber Incident in Past Year
Over half (54%) of respondents admitted their organization experienced a cybersecurity incident in the past year. Of these, 52% said the incident cost the organization at least $300,000.
The most common types of attacks experienced by companies were:
- Malware (76%)
- Phishing (54%)
- Credential stuffing (37%)
- Supply chain and social engineering attacks (32%)
- Cryptojacking (27%)
Nearly three-quarters (73%) of organizations believe they are likely to be disrupted by a cybersecurity incident in the next 12-24 months.
Close to two-thirds (62%) identified external actors as their biggest cyber threat, with 31% highlighting internal actors. This marked a significant shift from 2023 when the two were seen as almost equal threats, noted Cisco.
Another notable finding from the report was the impact of the cyber skills gap on organizations. Nearly half (46%) of organizations revealed they had more than 10 unfilled cybersecurity roles on their teams at the time of the survey.
On March 18, Microsoft reported that just 13% of UK organizations are resilient to cyber-attacks, with the remainder either vulnerable (48%) or at high risk (39%) of damaging cyber-incidents.
