Russian state-sponsored media organization RT, formerly Russia Today, has used AI-powered software to create authentic-looking social media personas en masse for the last two years.
The software, known as Meliorator, is an AI-enabled bot farm generation and management software that has been used to disseminate disinformation on social media about several countries, including the US, Poland, Germany, the Netherlands, Spain, Ukraine and Israel.
This according to a joint advisory published on July 9 by several government agencies in the US, Canada and the Netherlands.
The Meliorator campaign was observed as early as 2022. Although the tool was only identified on X, the analysis indicated that the developers intended to expand its functionality to other social media platforms, including Facebook and Instagram.
Meliorator has been used to spread disinformation on various topics, including the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
These included videos in which President Putin justified Russia’s actions in Ukraine and claimed that some regions of Poland, Ukraine, and Lithuania were “gifts” to those countries from the Russian forces that liberated them from Nazi control during World War II.
Meliorator’s Features
Meliorator offers a range of features, including:
- Use of AI to creating authentic appearing social media personas en masse
- Deploying typical social media content
- Mirroring disinformation of other bot personas
- Perpetuating the use of pre-existing false narratives to amplify malign foreign influence
- Formulating messages to include the topic and framing based on the specific archetype of the bot
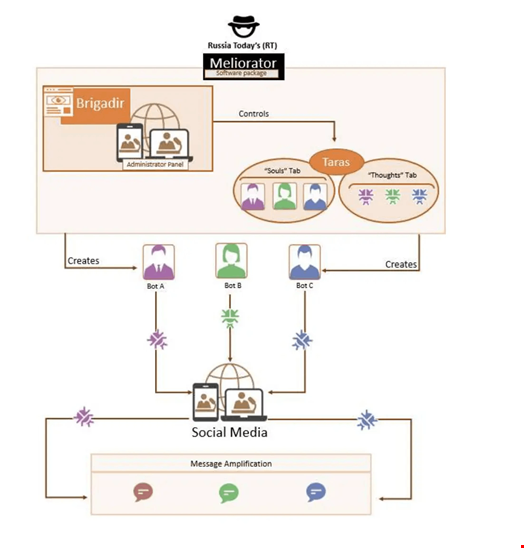
The software package includes an administrator panel called ‘Brigadir’ and a back-end seeding tool called ‘Taras.’
The Meliorator developers used Redmine, a free and open-source web application designed for project management, to build it.
Typically, Meliorator users connect via virtual network computing (VNC) connections.
According to an associated US Department of Justice (DoJ) press release, the bot farm created with Meliorator was developed by an individual identified as Individual A. This person worked as the deputy editor-in-chief at RT.
How Russian Media Uses Meliorator
On Meliorator, the false identities created as a basis for the bots are called ‘souls’ and automated scenarios or actions that can be implemented on behalf of the bots are called ‘thoughts.’
Read more: Cyber Threat Intelligence Pros Assess AI Threat Technology Readiness Levels
The personas associated with the Meliorator tool are capable of the following actions:
- Deploying typical social media content, such as generating original posts, following other users, “liking,” commenting, reposting and obtaining followers
- Mirroring disinformation of other bot personas through their messaging, replies, reposts and biographies
- Perpetuating the use of pre-existing false narratives to amplify Russian disinformation
- Formulating messaging to include the topic and framing based on the specific archetype of the bot
How Social Media Platforms Can Fight Against Bot Farms
Several features within Meliorator allow bots to seem authentic and avoid detection on social media.
For instance, most of the accounts followed by the bot personas boasted more than 100,000 followers, which is necessary for a bot persona to avoid detection when interacting with other accounts.
Other more technical measures are also built within the software to avoid detection, such as the ability to obfuscate an IP address and bypass dual-factor authentication,
Despite these techniques, intelligence agencies have provided a list of mitigation recommendations for social media organizations to reduce the impact of Russian state-sponsored actors using their platforms in disinformation campaigns.
These include:
- Implementing processes to validate that accounts are created and operated by a human person who abides by the platform’s respective terms of use
- Reviewing and making upgrades to authentication and verification processes
- Implementing protocols for identifying and subsequently reviewing users with known suspicious user agent strings
- Making user accounts Secure by Default by using default settings such as multifactor authentication (MFA), default settings that support privacy, removing personally identifiable information shared without consent and clear documentation of acceptable behavior
In relation to the joint action by intelligence agencies, the US DoJ announced the seizure of two related domain names and 968 social media accounts used in malign influence operations.
